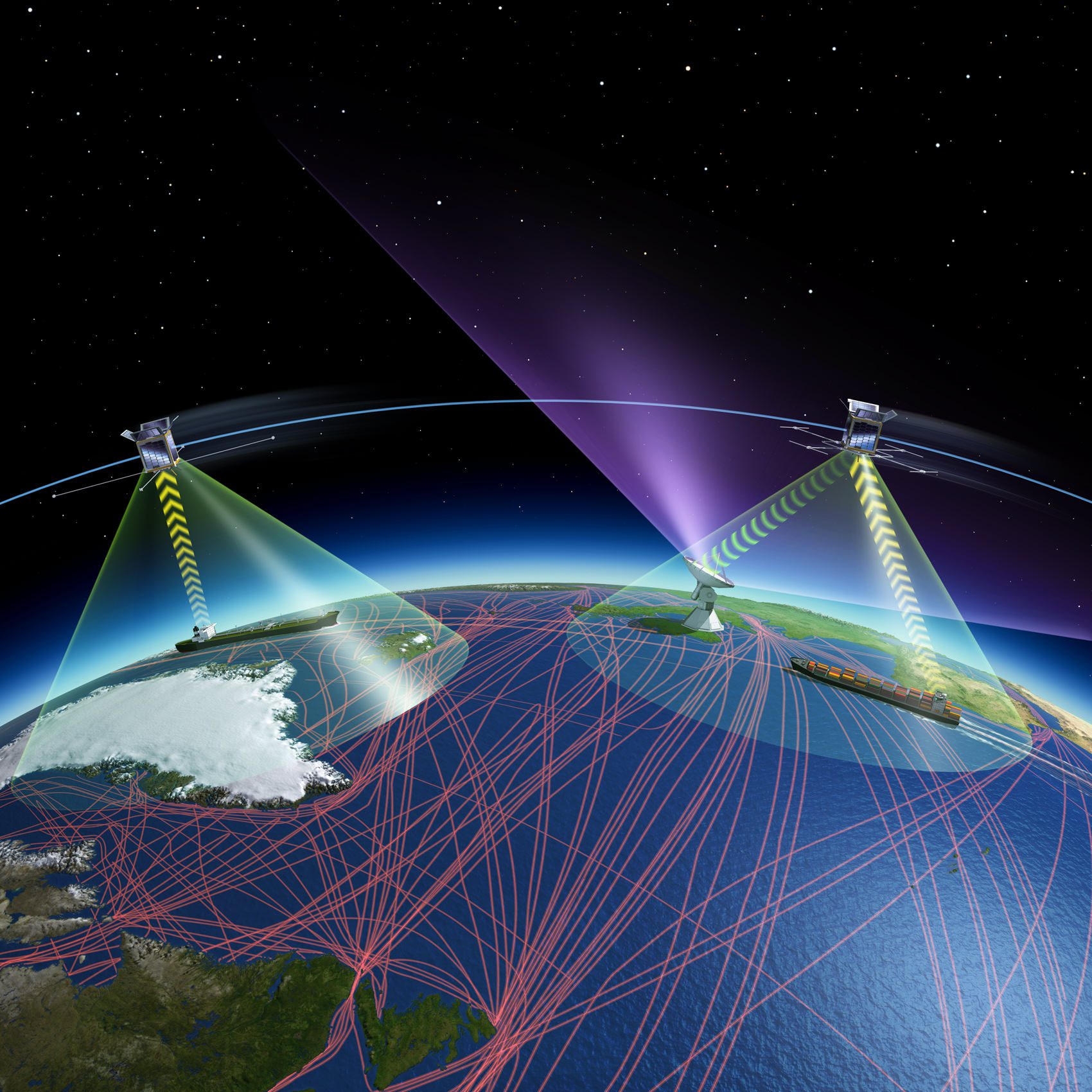
As the global community strives to achieve the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030, sustainable shipping emerges as a critical area of focus. To support the industry’s transition towards a sustainable future, the European Space Agency (ESA) is leveraging satellite navigation, telecommunications (including satellite 5G), and Earth observation data through its Blue Worlds Task Force to support maritime technology including autonomous shipping.
In Europe alone, the ‘blue economy’ represents roughly 5.4 million jobs and a gross added value of almost €500 billion a year so the ESA’s Blue Worlds Task Force is interested in exploring how space can support maritime technology including autonomous shipping.
Just as driverless cars are poised to revolutionize the automotive industry, ships without onboard captains could transform the shipping sector. However, there are potential challenges and drawbacks associated with autonomous shipping. One significant issue is the limited collaboration between the military and commercial sectors. The US Navy, a leader in development spending for autonomous technologies, is not sharing all its knowledge with the commercial sector due to the classified nature of autonomous warships. This lack of information-sharing could hinder the progress of the commercial shipping industry.
NASA and the US Space Force have the potential to contribute significantly to the development of autonomous shipping, leveraging their expertise in space technology and satellite systems but, as these organizations are more closely connected to the US Military, they may follow the lead of the US Navy in prioritizing military applications and withholding certain classified information from the commercial sector. Consequently, the sharing of knowledge and technology between military and commercial entities in the United States may be limited, which could potentially hinder the progress of autonomous shipping in the commercial realm.
Autonomous shipping relies on dependable, accurate, and continuously available navigation systems. ESA’s Discovery & Preparation program supports research into enhancing existing satellite navigation systems to enable autonomous shipping. Studies have investigated the potential of satellite data to fill gaps in anti-collision systems, complement ground-based sensors, and ensure worldwide coverage.
In addition to ESA’s efforts, various academic institutions, maritime startup technology groups, and large companies are also involved in the development and promotion of sustainable and autonomous shipping. Notable examples include academic MIT’s robotics labs, SeaAhead, Sea Machines, and Kongsberg. Others like blksail, Nautilus Labs, FreightFlows and SailPlan are focusing on big data and AI to improve shipping efficiencies and solve climate problems.
In 2017, ESA signed an agreement with Rolls-Royce to explore how space technology could contribute to the development of autonomous and remote-controlled ships. The partnership has since focused on developing and validating new ship-to-shore communication systems, part of ESA’s Satellite for 5G (S45G) initiative. This integrated space-and-ground service will enable the operation of commercial autonomous shipping while also driving innovation in commercial marine vessels, cargo logistics, and smart ports.
While many organizations are interested in developing and implementing autonomous shipping technologies, providing a clear timeline for widespread adoption is challenging. The shipping industry is generally slow to adopt change, and regulatory agencies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and the United States Coast Guard (USCG) can take time to develop new regulations. Furthermore, venture capitalists tend to underinvest in hardware solutions and commercial shipping, which may slow progress in this sector.
By welcoming assistance from space and fostering collaboration between various organizations, stakeholders, and sectors, the shipping industry can overcome these challenges and make strides toward a more sustainable future. ESA’s Blue Worlds Task Force is actively working with Member States to determine how ESA-developed technologies, products, and programs can help address the challenges related to safe and efficient autonomous navigation of the seas. Utilizing space technology and promoting partnerships could help deliver a more sustainable shipping industry and contribute to the overall health of our planet.
Editorial Standards · Corrections · About gCaptain

 Join The Club
Join The Club