A new study has highlighted an unexpected consequence of reduced shipping emissions: a sudden and significant increase in global warming.
Human activities have long influenced the Earth’s climate, primarily through altering the atmospheric composition. This change generates what is known as “radiative forcing,” referring to the change in energy within the Earth’s atmosphere due to factors like greenhouse gases, which can affect climate change.
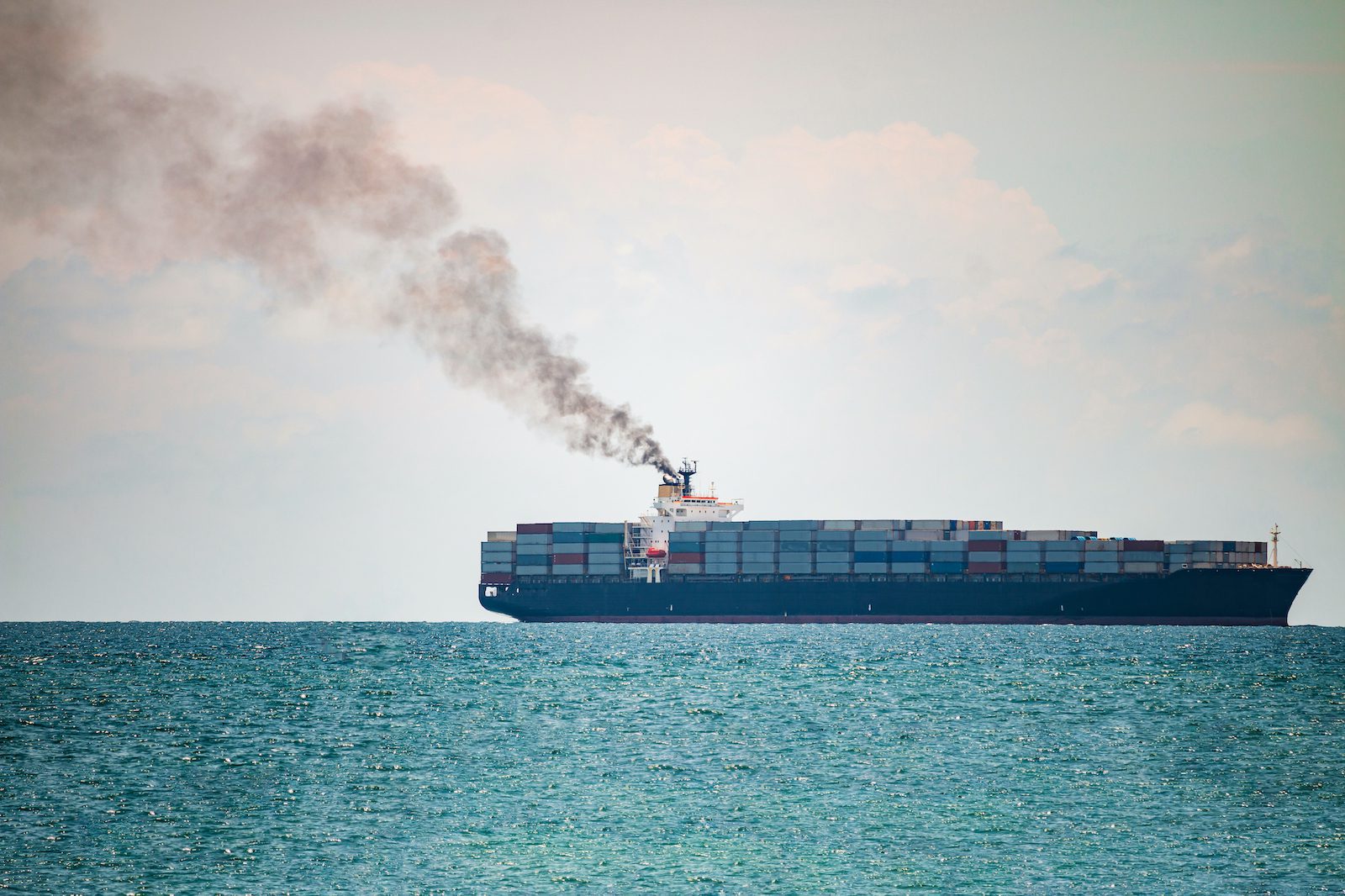
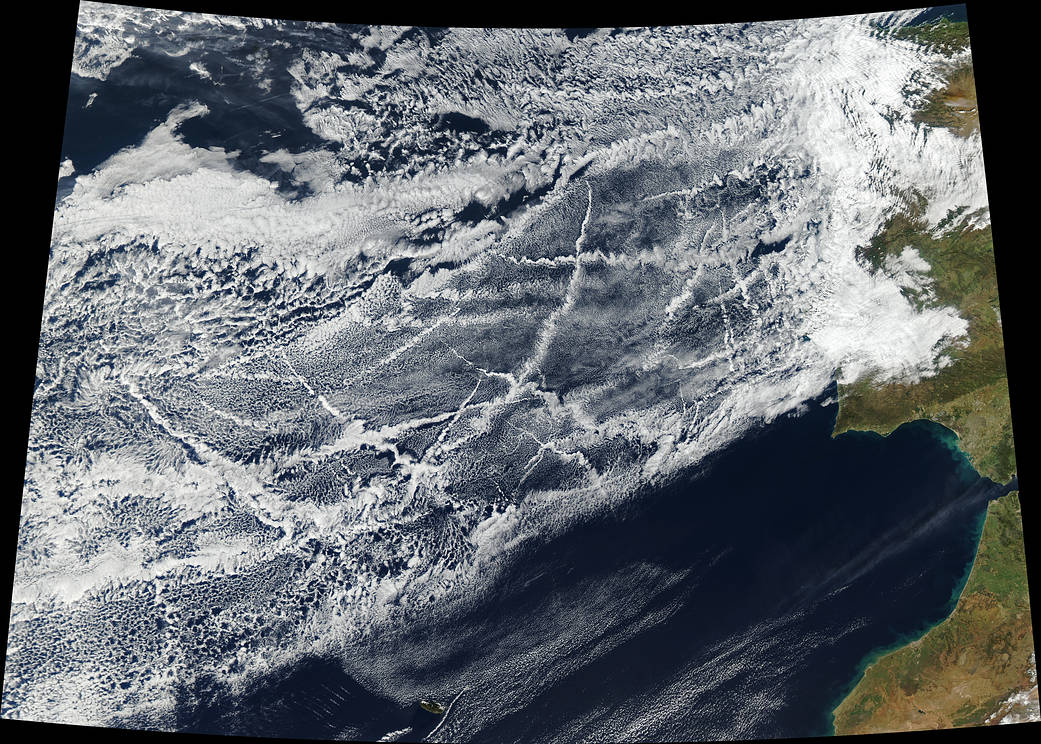
The warming impact of human-produced greenhouse gases has been somewhat counterbalanced by the cooling effect of human-made aerosols. However, in 2020, the International Maritime Organization’s low sulphur fuel regulations reduced the maximum sulfur content of bunker fuel burned by the global fleet of ships from 3.5% to 0.5% to benefit public health, leading to an abrupt 80% reduction in sulfur dioxide emissions from international shipping.
This unexpected change has resulted in what researchers describe as an ‘inadvertent geoengineering termination shock’ with a global impact. The sudden decrease can temporarily accelerate global warming by dimming clouds across the global oceans.
Scientists estimate that the regulation has led to a significant increase in radiative forcing across the world’s oceans. The study warns this increase could potentially double, or even triple, the warming rate in the 2020s compared to the rate since 1980.
The warming effect aligns with the recent observed temperature rise in 2023 and is projected to make the 2020s exceptionally warm. The radiative forcing is equivalent to 80% of the measured increase in planetary heat uptake since 2020, creating a strong hemispheric contrast with important implications for changing precipitation patterns, according to the study.
The study suggests that marine cloud brightening, where marine low clouds are seeded with aerosols to become brighter, temporarily cooling the climate, may be a viable geo-engineering solution. Of course, this comes with its own unique challenges.
The study, titled Abrupt reduction in shipping emission as an inadvertent geo-engineering termination shock produces substantial radiative warming, can be found in Communications Earth & Environment.
Editorial Standards · Corrections · About gCaptain

 Join The Club
Join The Club