Yemen’s Houthis Target MSC Ship in Gulf of Aden
DUBAI, April 25 (Reuters) – Yemen’s Houthis said they targeted the MSC Darwin ship in the Gulf of Aden on Thursday, as the Iran-aligned group resumed attacks on commercial ships in the Red Sea...
Researchers at the University of Houston have uncovered the largest single volcano on earth, laying thousands of feet below the surface of the Pacific Ocean.
Covering an area roughly equivalent to the state of New Mexico, or about 120,000 square miles, the volcano, dubbed the Tamu Massif, is nearly as big as the giant volcanoes of Mars, placing it among the largest in the Solar System. By comparison, Hawaii’s Mauna Loa – the largest active volcano on Earth – is approximately 2,000 square miles, or roughly 2 percent the size of Tamu Massif.
The discovery of the volcano is actually nothing new. William Sager, a professor in the Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences at UH, first began studying the volcano about 20 years ago at Texas A&M’s College of Geosciences. However, until now, it was not known whether Tamu Massif was a single volcano, or a composite of many eruption points.
But by integrating several sources of evidence, including core samples and data collected on board the JOIDES Resolution research vessel, the researchers have confirmed that the mass of basalt that constitutes Tamu Massif did indeed erupt from a single source near the center.
“Tamu Massif is the biggest single shield volcano ever discovered on Earth,” Sager said. “There may be larger volcanoes, because there are bigger igneous features out there such as the Ontong Java Plateau, but we don’t know if these features are one volcano or complexes of volcanoes.”
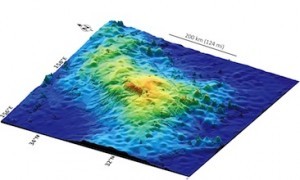

The Tamu Massif is located about 1,000 miles east of Japan in the so-called Shatsky Rise, an underwater mountain range that is said to have formed 130 to 145 million years ago by the eruption of several underwater volcanoes.
Tamu Massif stands out among underwater volcanoes not just for its size, but also its shape.
“It’s not high, but very wide, so the flank slopes are very gradual,” Sager said. “In fact, if you were standing on its flank, you would have trouble telling which way is downhill. We know that it is a single immense volcano constructed from massive lava flows that emanated from the center of the volcano to form a broad, shield-like shape. Before now, we didn’t know this because oceanic plateaus are huge features hidden beneath the sea. They have found a good place to hide.”
Its top lies about 6,500 feet below the ocean surface, while much of its base is believed to be in waters that are almost four miles deep.
“It’s shape is different from any other sub-marine volcano found on Earth, and it’s very possible it can give us some clues about how massive volcanoes can form,” Sager said. “An immense amount of magma came from the center, and this magma had to have come from the Earth’s mantle. So this is important information for geologists trying to understand how the Earth’s interior works.”
Not to worry however… the volcano has been extinct for millions of years, the researchers say.
The project was funded by the National Science Foundation, both through direct grants and through its Integrated Ocean Drilling Program, an international research program dedicated to advancing scientific understanding of the Earth through drilling, coring and monitoring the subsea floor.
Join the gCaptain Club for curated content, insider opinions, and vibrant community discussions.


Join the 105,881 members that receive our newsletter.
Have a news tip? Let us know.
Access exclusive insights, engage in vibrant discussions, and gain perspectives from our CEO.
Sign Up




Maritime and offshore news trusted by our 105,881 members delivered daily straight to your inbox.



Essential news coupled with the finest maritime content sourced from across the globe.
Sign Up