In the 4th, and final chapter of this series on shipping efficiency technology, improvement in Operation and Maintenance procedures are considered.
A faster port turnaround time makes it possible to decrease the vessel speed at sea. This is mainly a benefit for ships with scheduled operations, such as ferries and container vessels. The turnaround time can be reduced for example by improving maneuvering performance or enhancing cargo flows with innovative ship designs, ramp arrangements or lifting arrangements.
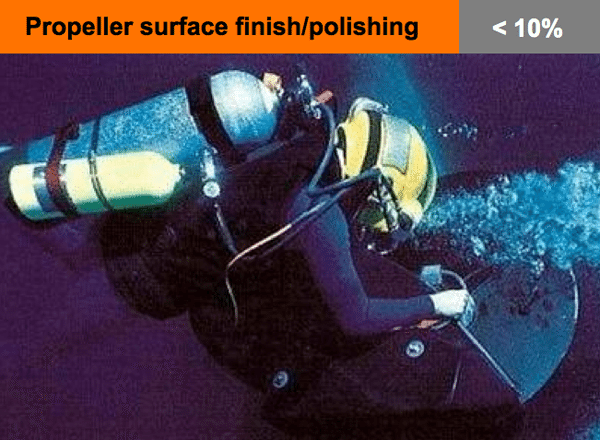

Regular in-service polishing is required to reduce surface roughness on propellers caused by organic growth and fouling. This can be done without disrupting service operation by using divers.
Up to 10% improvement in service propeller efficiency compared to a fouled propeller.
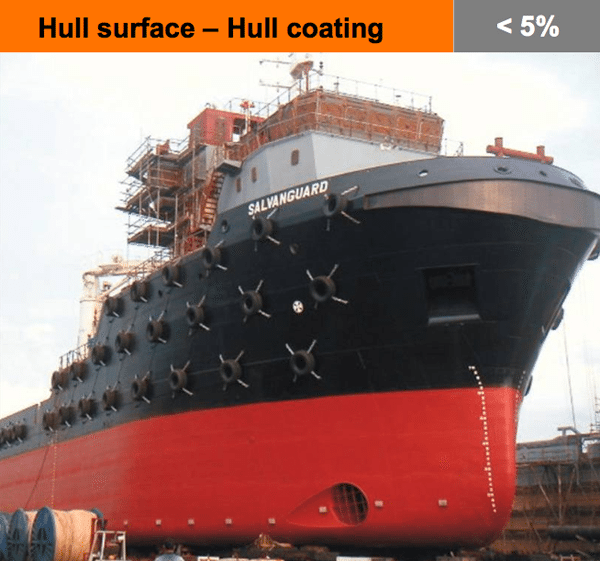
Modern hull coatings have a smoother and harder surface finish, resulting in reduced friction. Since typically some 50-80% of resistance is friction, better coatings can result in lower total resistance.
A modern coating also results in less fouling, so with a hard surface the benefit is even greater when compared to some older paints towards the end of the docking period.
Saving in fuel consumption after 48 months compared to a conventional hull coating:
- Tanker: ~ 9%
- Container: ~ 9%
- PCTC: ~ 5%
- Ferry: ~ 3%
- OSV: ~ 0.6%
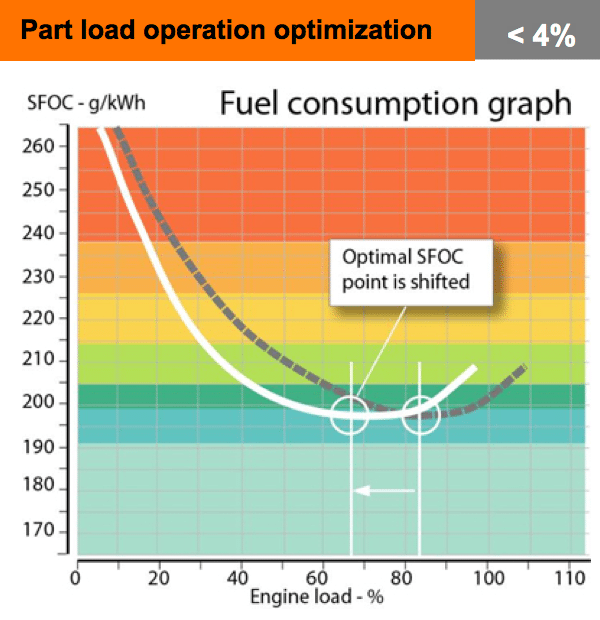
Engines are usually optimized at high loads. In real life most of them are used on part loads. New matching that takes into account real operation profiles can significantly improve overall operational efficiency.
New engine matching means different TC tuning, fuel injection advance, cam profiles, etc.

Reducing the ship speed an effective way to cut energy consumption. Propulsion power vs. ship speed is a third power curve (according to the theory) so significant reductions can be achieved. It should be noted that for lower speeds the amount of transported cargo / time period is also lower. The energy saving calculated here is for an equal distance travelled.
Reduction in ship speed vs. saving in total energy consumption:
- 0.5 kn –> – 7% energy
- 1.0 kn –> – 11% energy
- 2.0 kn –> – 17% energy
- 3.0 kn –> – 23% energy
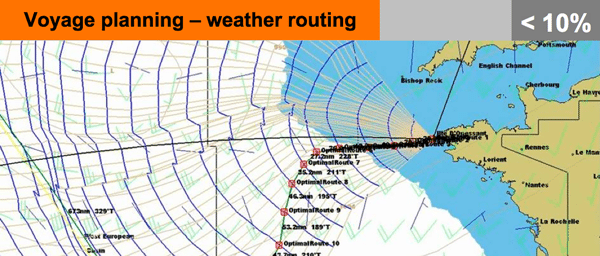
The purpose of weather routing is to find the optimum route for long distance voyages, where the shortest route is not always the fastest. The basic idea is to use updated weather forecast data and choose the optimal route through calm areas or areas that have the most downwind tracks. The best systems also take into account the currents, and try to take maximum advantage of these. This track information can be imported to the navigation system.
Shorter passages, less fuel.

The optimum trim can often be as much as 15-20% lower than the worst trim condition at the same draught and speed. As the optimum trim is hull form dependent and for each hull form it depends on the speed and draught, no general conclusions can be made. However by logging the required power in various conditions over a long time period it is possible to find the optimum trim for each draught and speed.
Or this can be determined fairly quickly using CFD or model tests. However it should be noted that correcting the trim by taking ballast will result in higher consumption (increased displacement). If possible the optimum trim should be achieved either by repositioning the cargo or rearranging the bunkers.
Optimal vessel trim reduces the required power.

Poor directional stability causes yaw motion and thus increases fuel consumption. Autopilot has a big influence on the course keeping ability. The best autopilots today are self tuning, adaptive autopilots.
Finding the correct autopilot parameters suitable for the current route and operation area will significantly reduce the use of the rudder and therefore reduce the drag.
Finding the correct parameters or preventing unnecessary use of the rudder gives an anticipated benefit of 1-5%.

A shipping company, with its human resources department, could create a culture of fuel saving, with an incentive or bonus scheme based on fuel savings. One simple means would be competition between the company’s vessels. Training and a measuring system are required so that the crew can see the results and make an impact.
Historical data as reference. Experience shows that incentives can reduce energy usage by up to 10%.
In a CBM system all maintenance action is based on the latest, relevant information received through communication with the actual equipment and on evaluation of this information by experts.
The main benefits are: lower fuel consumption, lower emissions, longer interval between overhauls, and higher reliability.
Correctly timed service will ensure optimum engine performance and improve consumption by up to 5%.
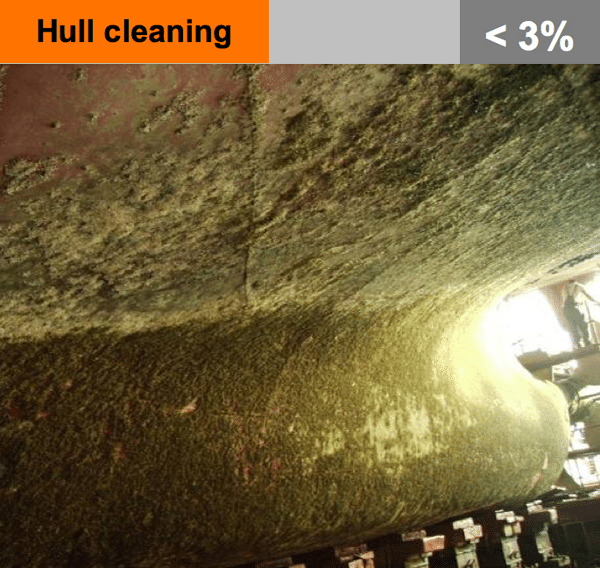

Algae growing on the hull increases ship resistance. Frequent cleaning of the hull can reduce the drag and minimise total fuel consumption.
Reduced fuel consumption:
- Tanker: ~ 3%
- Container: ~ 2%
- PCTC: ~ 2%
- Ferry: ~ 2%
- OSV: ~ 0.6%
Part 1: How to Design a More Efficient Ship
Part 2: How to Propel a More Efficient Ship
Part 3: Marine Engineering Technology for More Efficient Shipping
All information and images courtesy of Wärtsilä

 Join The Club
Join The Club






















