By Malte Humpert (gCaptain) –
For the first time the EU is targeting specific vessels part of Russia’s dark fleet created to circumvent the oil price caps. In total the latest measures include designation of eleven crude oil carriers and five oil product tankers.
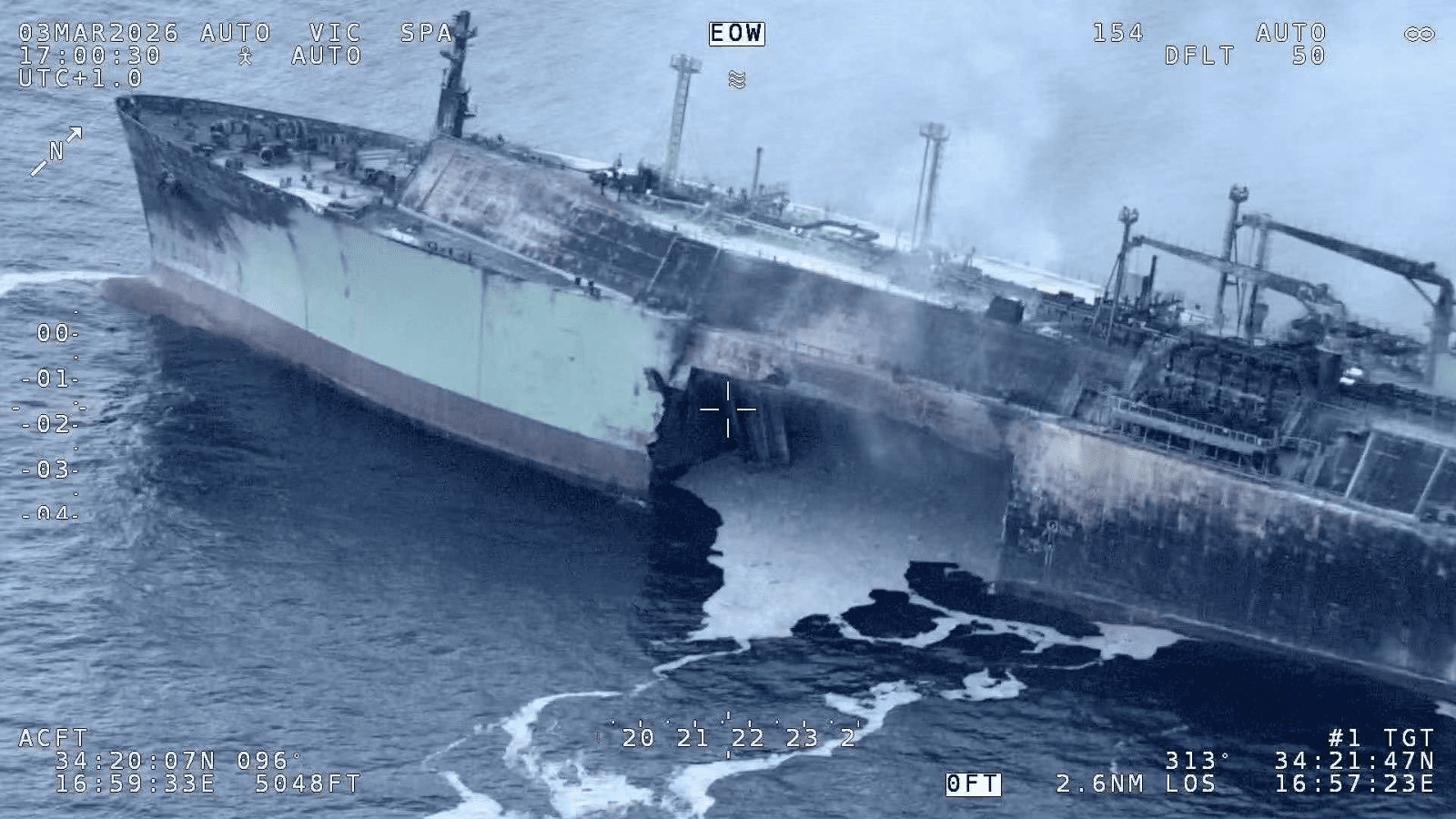
By relying on a dark fleet of aging and often poorly maintained vessels Russia follows deceptive shipping practices disregarding international standards, the EU states.
The batch of vessels carry a long list of deficiencies recorded during recent port inspections, including hull damage impairing seaworthiness, lack of civil liability for oil pollution damage, and impaired structural integrity in fuel tanks.
The oil tankers are routinely engaged in ship-to-ship transfer of crude to evade sanctions. Several vessels now sanctioned by the EU lack certification or planning documents for STS operations or plans for spill response.
The average age of the crude carriers exceeds 20 years, with some vessels approaching 30 years.
The five sanctioned product tankers similarly have a long record of fire safety and pollution prevention violations. Their average age also approaches 20 years.
List of sanctioned crude oil carriers and product tankers:
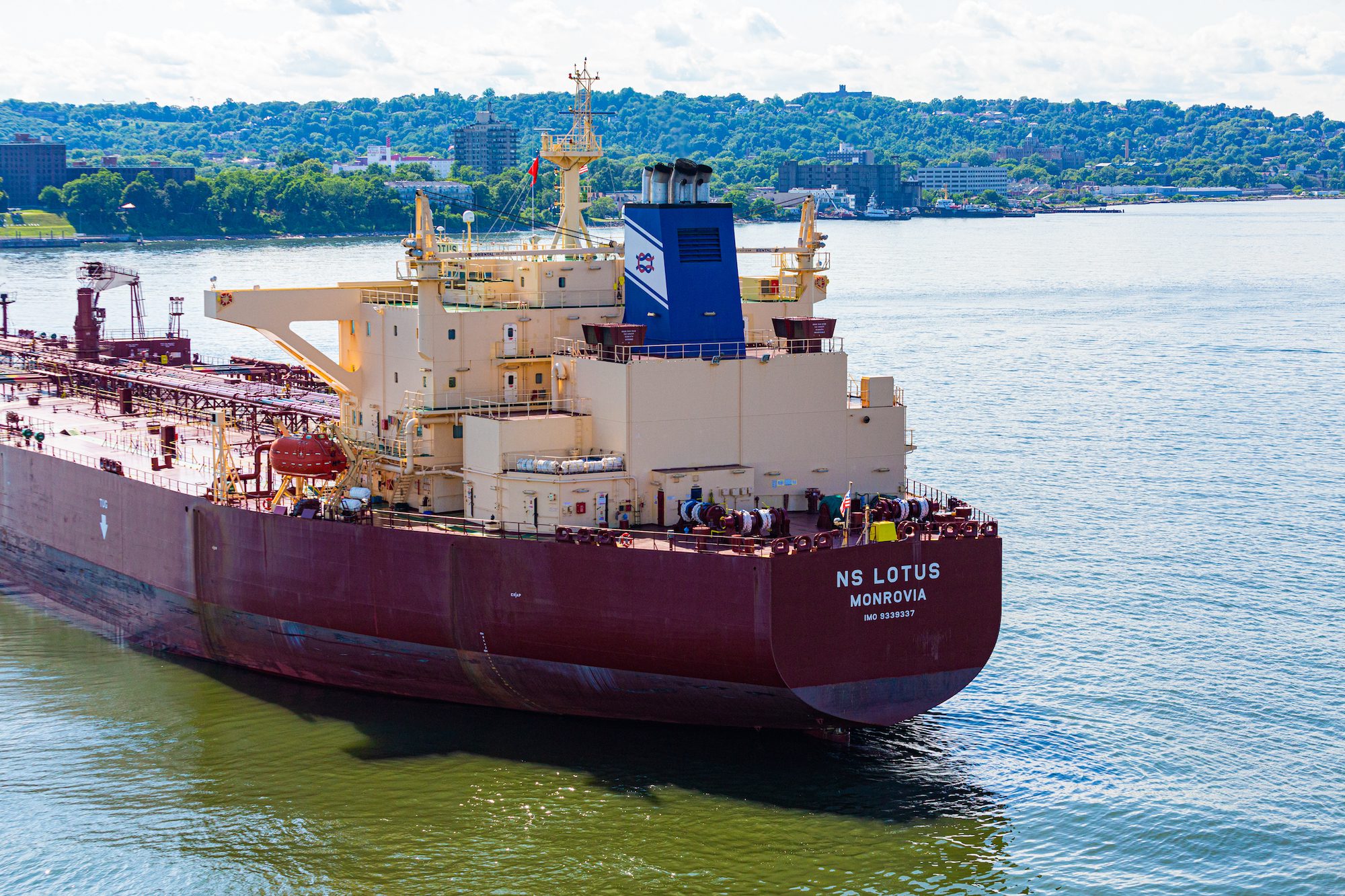
- ANDROMEDA STAR (IMO 9402471), NS LOTUS (IMO 9339337), HEBE (IMO 9259185), VELA RAIN (IMO 9331141), OCEAN AMZ (IMO 9394935), GALIAN 2 (IMO 9331153), ROBON (IMO 9144782), KEMEROVO (IMO 93128840), KRYMSK (IMO 9270529), NS CREATION (IMO 9312896), NS CAPTAIN (IMO 9341067).
- HANA (IMO 9353113), CANIS POWER (IMO 9289520), NS SPIRIT (IMO 9318553), SCF AMUR (IMO 9333436), BEKS AQUA (IMO 9277735)
The latest round of EU measures also targets maritime assets used to develop Russia’s energy sector.
Two massive 400-meter long floating storage units (FSU), the largest of their kind in the world, have been sanctioned. FSU Saam and Koryak are part of Russia’s logistics scheme to export liquefied natural gas (LNG) to Europe and Asia.
Russia’s largest LNG producer Novatek positioned the two FSU at each terminus of the Arctic Northern Sea Route, near Murmansk and in Kamchatka, in 2023. Built by South Korean shipyard Hanwha they are designed to hold 360,000 cubic meters of LNG. Without them Novatek will have to increasingly resort to ship-to-ship transfers.
In an effort to further impede construction of new LNG plants in Russia, EU measures also block three heavy lift vessels carrying modules manufactured in Chinese yards.
Two vessels by shipping company Red Box, Audax and Pugnax, previously sanctioned by the U.S., are now barred from entering EU ports further limiting their operations. A Chinese-owned vessel Hunter Star is also included in the new sanctions. Other Chinese heavy lift vessels continue to carry modules.
An additional six vessels were sanctioned for their role in carrying Russian military equipment and transporting stolen Ukrainian grain.
The latest sanctions also include a transshipment ban of Russian LNG across EU ports to take effect after a nine-months transition period. As a result Russia is expected to further increase its use of STS operations for LNG reloading in Russian or international waters.
Editorial Standards · Corrections · About gCaptain

 Join The Club
Join The Club